

Next: Primitive data types for
Up: Unit 04
Previous: Other primitive data types
Besides the types for representing integer numbers, in Java there are two
primitive data types for representing real numbers. Due to the way in which
real numbers are represented internally in memory, these numbers are also
called floating point numbers.
The data type for floating point numbers that is used by default in the Java
mathematical library is double.
| Type |
double |
| Dimension |
64 bit (8 byte) |
| Domain |
set of 264 positive and |
Minimum absolute value |
1.79769313486231570 . 10-308 |
| |
negative real numbers |
Maximum absolute value |
2.250738585072014 . 10+308 |
| |
|
Precision |
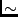 15 decimal digits 15 decimal digits |
| Operations |
+ |
sum |
| |
- |
difference |
| |
* |
product |
| |
/ |
division |
| Literals |
sequences of digits with decimal dot
optionally ending with a d (or D) |
| |
denoting values of the domain (e.g., 3.14 or
3.14d) |
| |
representation in scientific notation
(e.g., 314E-2 or 314E-2d) |
Example:
double pi, p2; // Declaration of variables of type double
pi = 3.14; // Use of literals
p2 = 628E-2d; // Use of literals
p2 = pi * 2; // Arithmetic expression


Next: Primitive data types for
Up: Unit 04
Previous: Other primitive data types